Currently Empty: $0.00

Network security is like a worldwide chess game; the more strategic your moves, the stronger your defense.
In the face of advancing technology and increasing cyber threats, network security has become critical – a matter of survival for the sustainability of our security.
Fundamentals of Network Security
Network security is the process of protecting information and data from unauthorized access, attacks and breaches. The main objective is to protect the fundamental principles of integrity, confidentiality and availability. This includes not only data security but also hardware and software protection.
An effective network security strategy should include layered defense mechanisms, with each layer of security providing different controls to prevent or detect threats. Particularly important is a multi-pronged approach, combining physical, technical and administrative aspects. This ensures comprehensive protection against internal threats as well as external threats.
Ensuring network security is a continuous process and requires constant review and updating of the security infrastructure. As each new technology and threat emerges, it is critical that defenses evolve.
If you would like to learn more about an effective network security strategy, you can check out our ‘Cybersecurity Basics Training’ course.
Definition of Network Security
Network security is a set of processes and policies that protect computer networks, ensuring the security of data and resources.
Millions of cyber-attacks occur every year, making network security even more important.
This process, in which each security layer includes specialized defense mechanisms that increase resilience against attacks, gives the ability to actively detect and respond to threats.
The ability to respond quickly to incidents – minimizing damage by reducing response time – is a key element of network security.
If you want to learn how to create network security policies, you can take a look at our article on ‘Cyber Defense SOC Expertise’.
Why is Network Security Important?
Network security is vital to protecting corporate assets and data. Security breaches can lead to reputational damage and financial losses.
Cybercrime is on the rise and threats such as data theft, phishing and ransomware attacks are constantly evolving. The integration of layered security approaches, network security policies and proactive monitoring mechanisms is essential to prevent these threats. An effective network security strategy requires preparedness not only for existing threats but also for potential future threats.
In addition, regulatory and legal obligations also increase the importance of network security. Compliance with national and international legislation must be ensured to protect personal data, trade secrets and intellectual property rights.
Network security is also part of business continuity and disaster recovery planning. Creating a network structure that is resilient against data loss and system crashes that may occur due to natural disasters, human errors or technical failures is critical for organizations to continue their operations smoothly. This resilience is a factor that reinforces customer confidence and provides an advantage in market positioning.
For more information about cybercrimes and how to protect against them, read our article ‘Cybercrimes: The Most Common Internet Crimes in Turkey‘ for more information.
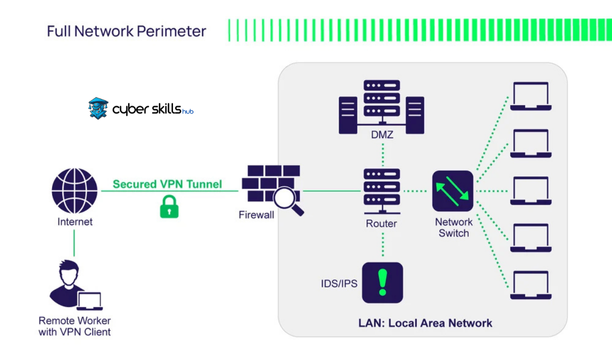
Threats and Vulnerabilities
Threats such as cyber attacks, malware and denial of service attacks (DDoS) are among the threats to network security. Strong defense mechanisms must be developed to protect against these threats.
Vulnerabilities are caused by internal factors such as software bugs, configuration errors and lack of security updates. These weaknesses put information security at risk by making the system more vulnerable to external threats.
Regularly identifying and remediating security vulnerabilities is a fundamental step in ensuring network security.
Common Types of Cyber Attacks
Phishing Attacks aim to lure users to websites that appear to be legitimate but are malicious in order to capture their information. These types of attacks often use emails that are designed to look like they come from a trusted source.
For information about protection methods against phishing attacks, please visit our article ‘What is Smishing: Cyber Threats and Protection Methods‘ for more information.
Ransomware attacks have been increasing rapidly in recent years. In this type of attack, malicious actors block access to a system or data, or encrypt it, forcing victims to pay a ransom.
DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) attacks aim to send an excessive amount of fake traffic to a network or server, making the targeted system unavailable. This can cause service disruption, causing financial and reputational damage to organizations.
Advanced persistent threats such as APT (Advanced Persistent Threat) are long-term and focused cyber espionage campaigns. In these attacks, attackers often aim to remain undetected within the network and steal valuable data.
Software vulnerability exploitation attacks are forms of attacks that aim to infiltrate systems using known or unknown software bugs (exploits). This is accomplished through vulnerabilities in outdated software.
Sources of Vulnerabilities
Vulnerabilities in network security can originate from a variety of sources and range widely. In particular, software bugs lead to system vulnerabilities. Incorrect configurations or inadequate security policies can also trigger these vulnerabilities. These elements that threaten the system are called vulnerabilities.
Human factor is known as one of the most common sources of vulnerabilities. User errors, weak passwords and impulsive clicks set the stage for attacks such as social engineering. In addition, lack of training prevents employees from following security procedures, leading to vulnerabilities.
Periodic updates and regular maintenance are essential to ensure the security of hardware and software. Outdated systems, outdated security protocols and uncorrected software bugs create easy targets for cyber attackers. These vulnerabilities can be exploited for malicious activities and lead to high-level security threats.
Vulnerabilities of third-party services pose significant risks to the complex systems involved in network security. Supply chain attacks are one of these risks. Vulnerable third-party software or hardware can cause serious security vulnerabilities on systems connected to your network.
Finally, evolving technology and new application developments can introduce new vulnerabilities. Therefore, it is imperative for network security professionals to continuously train and stay up to date. Understanding the changing threat landscape and implementing appropriate security controls is critical to minimizing vulnerabilities.
Methods to Ensure Network Security
Beginning of ensuring network security is to implement a strong and dynamic access control policy. Once users, devices and network segments are discovered and classified, each of these elements is assigned the necessary permissions based on the principle of least privilege. This ensures that each user and device has access to the data and resources they need, without unnecessarily high privileges. Role-based access control (RBAC) is critical in configuring this process and prevents over-authorization, which can inadvertently or intentionally cause major security breaches.
Furthermore, monitoring and analyzing traffic by observing your network is essential for anomaly detection and preventive measures. Behavior-based analysis can alert security teams by revealing unexpected network activity. This type of analysis enables next generation firewalls (NGFW) and advanced threat protection (ATP) solutions to proactively detect and respond to vulnerabilities in your network.
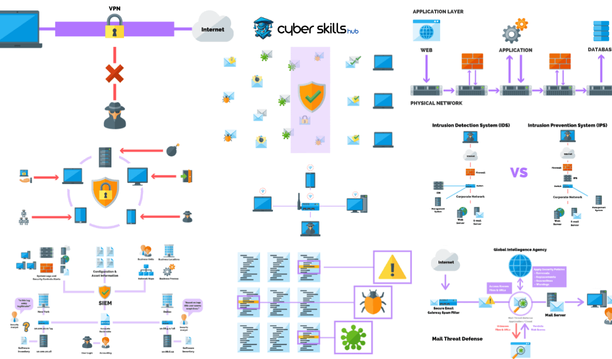
Firewalls and Antiviruses
Firewalls provide a line of defense that controls access to your network and blocks unauthorized traffic. Antivirus programs detect and protect against malware.
- Firewall Types: Firewalls include packet filtering, stateful, proxy-based, and cross-layer firewalls (NGFW).
- Antivirus Protection Methods: Antivirus software uses signature-based detection, behavioral analysis (heuristic), cloud-based analysis and sandboxing techniques.
- Integration and Management: For an effective network security strategy, it is important that firewalls and antiviruses work in integration with other security infrastructure and are controlled by a centralized administration. Firewalls act as a border security mechanism, protecting against internal and external threats, while antiviruses isolate potential malware.
Both systems should be continuously updated and proactive against new threats, creating a security framework to keep the system protected.
To learn how to integrate and manage firewalls and antiviruses, check out our article ‘What is a Firewall and How Does it Work?
Access Control and Encryption
Access control manages access to resources by authorized users and prevents unauthorized access. Encryption protects data against unauthorized access.
- Authentication: Authentication of the user’s identity.
- Authorization: Determining and enforcing access permissions.
- Access Rights Management: Defining the conditions under which users can access data and resources.
- Role Based Access Control (RBAC): Setting access permissions for users based on roles.
- Encryption Protocols: Secure protocols used during data transmission, such as SSL/TLS.
- Data Encryption Standards: Encryption standards used for data storage and transmission, such as AES, DES.
A strong policy and process is necessary for effective implementation of access control and encryption mechanisms.
As part of these processes, the management and storage of encryption keys must also be handled with care. Secure encryption is a cornerstone of network security.
For more details on the importance of access control and encryption, see our article ‘How to Develop Application Security Strategies’.
Best Practices for Network Security
To improve network security, strong password policies must be effectively implemented. This is the first line of defense against cyber attacks.
For example, two-factor authentication (2FA) can significantly reduce unauthorized access to systems. Security awareness training for employees should be provided regularly, which minimizes human vulnerabilities.
Finally, periodic security audits and penetration tests are critical in determining the state of the network and identifying potential vulnerabilities.
Updates and Patch Management
One of the most important ways to protect against ever-evolving threats in network security is to regularly update systems.
- Patch Scheduling: Identifying and scheduling the latest security patches.
- Risk Assessment: Assessing the potential impacts of the patch before it is applied.
- Test Processes: Checking patches in test environments before they are applied to live systems.
- Patch Deployment: Integration of approved patches into the system without errors.
- Post-Monitoring: Monitoring of processes and systems after the patch is applied. Another issue to be considered in patch management is the timing and coordination of the implementation.
Automated patch management systems increase the efficiency and effectiveness of the process, while minimizing human error and keeping safety levels consistently high.
Security Policies and Education
Security policies are the pillar of network security and regulate the use of IT within the organization. These policies need to be specific and clear.
To create an effective security policy, the needs of all parts of the organization should be taken into account and shaped according to security risks. These policies should include technical measures as well as rules of conduct for personnel.
Safety training programs are critical for employees, who are the implementers of the policies, to understand and adopt these rules. Trainings should be updated at regular intervals and keep staff safety awareness alive at all times.
In addition to introducing cyber threats, security trainings should also provide practical information on how to ensure security in the daily workflow. Employees should be empowered to recognize threats and react appropriately.
Developing a safety culture in an organization is the responsibility of all employees, not just the safety team. Safety trainings reinforce this awareness.
To create a strong security policy in your organization and to get information about training programs, you can review our ‘Cyber Security Training: Specialize in the Sector‘ content.
Frequently Asked Questions on Network Security
What is Network Security?
Network security is the process of protecting computer networks and data from unauthorized access, attacks and breaches. Its main purpose is to ensure information integrity, confidentiality and availability.
Why is Network Security Important?
Network security ensures the protection of corporate data and assets and prevents reputational and financial losses. It also supports compliance with legal obligations and business continuity.
What are the Main Threats to Network Security?
Major threats to network security include malware, denial of service attacks (DDoS), phishing and ransomware attacks.
What Methods Are Used to Ensure Network Security?
Firewalls, antivirus programs, access control systems and encryption technologies are used to ensure network security. Updates and patch management are also important.
How Do Firewall and Antivirus Software Work?
Firewalls control access to your network by blocking unauthorized traffic. Antivirus software detects and protects against malware.
What is Access Control and Encryption?
Access control regulates access to resources by authorized users, while encryption protects data from unauthorized access.
What are the Best Practices for Network Security?
Best practices for network security include strong password policies, two-factor authentication, regular security training and penetration testing.
Why Patch Management is Important?
Patch management protects systems against current threats by closing vulnerabilities. Regular patching is critical to the sustainability of network security.
How to Integrate Security Policies and Education?
Security policies are tailored to organizational security needs and integrated by providing regular security training to all employees. These trainings improve employees’ ability to recognize threats and react correctly.







