Currently Empty: $0.00
What is Domain Name System Security Extensions (DNSSEC) and How Does It Work? Detailed Guide

Security and reliability are becoming more and more important in the Internet world. In this context, DNSSEC (Domain Name System Security Extensions) brings an additional layer of security to the DNS system, which forms the basis of online communication. DNSSEC protects users from potential threats by authenticating websites and protecting the integrity of DNS data.
In this guide, we will take a detailed look at what DNSSEC is and how it works. Firstly, we will examine the basic function and working principle of DNS. Then, we will explain the reasons for the emergence and purposes of Domain Name System Security Extensions. Finally, we will explain the technical aspects and working mechanism of DNSSEC in detail. This information will be an important resource for those who want to be more aware of internet security.
What is DNS and how does it work?
Definition of DNS
DNS stands for ‘Domain Name System’ and can be translated into Turkish as ‘Domain Name System’. DNS, which is described as the telephone directory of the Internet, is a system that translates domain names into IP addresses. While this system allows users to access websites using catchy domain names, it performs the conversion process to IP addresses that computers understand.
DNS Resolution Process
The DNS resolution process involves steps that take place in the background when you visit a website:
- The user enters a domain name in the browser (for example, www.example.com).
- This request is converted into a DNS query by the DNS client.
- The query is usually sent to the DNS server of the internet service provider (ISP).
- The DNS server finds the IP address where the domain name is registered.
- The found IP address is sent back to the user’s device.
- The browser loads the website by connecting to this IP address.
This process is completed in milliseconds and users are often unaware of it.
Importance of DNS
The importance of DNS in the internet world is revealed at the following points:
- Ease of Use: DNS allows us to use understandable domain names instead of remembering complex IP addresses.
- Efficiency: DNS caching allows frequently visited sites to load faster.
- Load Distribution: DNS can balance the load by directing traffic to different servers.
- Security: Additional security protocols, such as Domain Name System Security Extensions, provide protection against attacks that can occur through the DNS.
DNS is one of the cornerstones of the internet infrastructure and ensures that online communication takes place seamlessly. Without this system, our modern internet experience would be much more complex and cumbersome.
Emergence and Purpose of DNSSEC
Vulnerabilities of Traditional DNS
DNS was invented by Paul Mockapetris in 1983 as one of the cornerstones of the Internet. The first DNS server was called Jeeves, and the system was incorporated into internet standards by the IETF (Internet Engineering Task Force) in 1986. However, as the popularity of DNS grew, security vulnerabilities began to emerge.
In the early 1990s, a major vulnerability called ‘cache poisoning’ was discovered by Steve Bellovin. This discovery drew attention to the security problems of DNS and raised concerns about internet security. With the publication of Bellovin’s findings in 1995, serious work began on DNS security.
Reasons for the Development of DNSSEC
DNSSEC (Domain Name System Security Extensions) was developed to address the security vulnerabilities of DNS and protect Internet users from various threats. These threats include DNS poisoning, spoofing attacks and man-in-the-middle attacks.
The main reasons for the development of Domain Name System Security Extensions are the following:
- Ensure data integrity
- Create an authentication mechanism
- Improving the security of DNS queries
- Increasing the trust of Internet users

Main Objectives of DNSSEC
The main goals of Domain Name System Security Extensions are to protect internet users by adding an additional layer of security to the DNS system. These goals can be summarised as follows:
- Ensuring the accuracy and integrity of DNS data
- Protect against forged or manipulated DNS data
- Increasing confidence in critical internet services such as e-commerce, online banking and e-mail
- Reducing the risk of becoming a victim of cybercrime
- Building infrastructure for new types of secure data processing
DNSSEC digitally signs DNS records using public key cryptography and creates a chain of trust. In this way, users can verify that the web pages or services they want to connect to are indeed correct. Full implementation of Domain Name System Security Extensions ensures the security of critical DNS queries, making internet communications more secure.
Working Principle of DNSSEC
DNSSEC aims to protect internet users from various threats by adding an additional layer of security to the DNS system. This system digitally signs DNS records using public key cryptography and creates a chain of trust. Here are the basic elements of the working principle of Domain Name System Security Extensions:
Digital Signatures and Public Key Cryptography
Domain Name System Security Extensions uses digital signatures based on public key cryptography to secure DNS information. This system works as follows:
- Each DNS domain uses a key pair consisting of a secret and a public key.
- The secret key is used to sign DNS data and is only available to the key holder.
- The public key is published in the DNS domain and is used to check the authenticity of signatures.
- Signed DNS records are stored in special records called RRSIG (Resource Record Signature).
- The public key, called DNSKEY, is required for the verification of signatures.
This system guarantees the integrity of DNS data and the authenticity of its origin. An important point is that DNSSEC does not encrypt traffic, but only proves the authenticity of the IP addresses pointed to by the domain name.
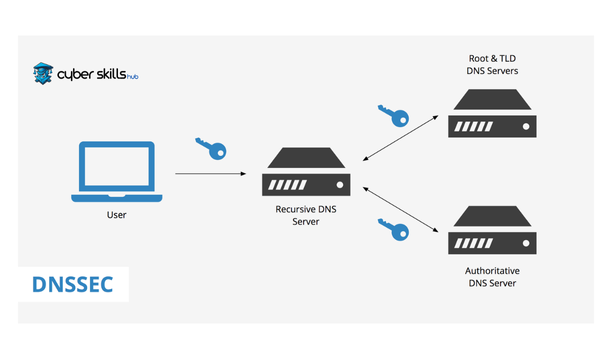
Chain of Trust Concept
For DNSSEC to be effective, all steps from the root domain to the final domain must be DNSSEC compliant. This creates a so-called chain of trust:
- Signing the root field is the starting point of the chain of trust.
- Each parent domain holds and verifies the public key of a child domain.
- Two key pairs are used, KSK (Key Signing Key) and ZSK (Zone Signing Key).
- The KSK is a long-term key and is usually renewed once a year.
- The ZSK is a short-term switch and is replaced more frequently.
- The KSK signs the ZSK and the ZSK signs the DNS records.
This hierarchical structure ensures security at all levels, creating a trusted chain starting from the root domain to the last domain.
DNSSEC Verification Process
The DNSSEC validation process is designed to increase the security of DNS queries:
- When a client sends a DNS query, RRSIG is also sent in the response.
- The DNS server verifies the signature using DNSKEY.
- If the query is for a non-existent record, NSEC (Next Secure) records are used.
- NSEC creates a sorting within the zone and NSEC records are created for each record.
- When a nonexistent record is queried, the DNS server authenticates by sending the corresponding NSEC record.
This process improves the security of DNS queries and protects against forged or manipulated DNS data. The full implementation of DNSSEC ensures the security of critical DNS queries, making internet communication more secure. If you want to improve yourself in the field of cyber security and step into this mysterious world, you can review our Cyber Security Training.
Conclusion
DNSSEC plays an important role in the security infrastructure of the Internet. This system helps protect users from potential threats by increasing the security of DNS queries. Using public key encryption and digital signatures, it ensures the accuracy and integrity of DNS data. Thus, it plays a major role in reducing the risk of becoming a victim of cybercrime.
As a result, full implementation of DNSSEC is crucial to making internet communications more secure. It helps to increase trust in critical internet services such as e-commerce, online banking and email. For internet users and administrators, understanding and implementing DNSSEC is an effective step in improving online security.
Frequently Asked Questions About DNSSEC
What purpose does DNSSEC serve?
DNSSEC, developed by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF), is an encryption mechanism designed to increase the security of DNS information. This system contributes to internet security by strengthening DNS protocol standards.
What is Cloudflare DNSSEC and what does it do?
Cloudflare ensures the security of DNS queries by offering DNSSEC (DNS Security Extensions) support. It also provides faster responses to users thanks to fast DNS servers and allows quick changes with the ability to change temporary DNS settings.







