Currently Empty: $0.00

DNS is like the internet’s telephone directory; each website has a name corresponding to its IP address.
When you type a website name into your internet browser, DNS translates it into an IP address and directs you to the correct server – the behind-the-scenes workings of this complex process are often overlooked.
DNS Basics
DNS, the Domain Name System, is a hierarchical and decentralized system for identifying devices and resources on the Internet. It is the cornerstone of the internet by mapping between web addresses (domain names) and their numerical equivalents, IP addresses. It translates a series of letters and words that users can easily hold in their heads into a numerical code that determines which server to connect to in the background.
The domain name system makes it possible to address and access millions of websites around the world. When you enter the name of a website in a browser, the request first reaches the DNS server closest to you. The DNS server queries the IP address of the requested domain name and sends this information back to you, allowing you unhindered access to the website you want. Although this process may go unnoticed by the user, it is an essential component of secure and fast internet access.
Definition and Functions of DNS
DNS (Domain Name System) is a name resolution service that translates user-friendly domain names into numeric IP addresses. It can be thought of as the telephone directory of the Internet. Through this parsing process, computers and other devices can easily access websites.
Vital for routing network traffic, DNS ensures that each website is assigned a unique “domain name”. Domain names are words that humans can easily remember, while IP addresses are the language that computers understand. DNS effectively brings these two different forms of addressing together.
Without DNS, internet traffic would be chaotic and unmanageable.
By processing millions of queries per second, DNS ensures that the internet runs smoothly. Whenever there is a request to access a website, DNS servers step in and map the domain name to the IP address of that website. For the end user, this happens in a matter of seconds and thus forms the basis of network connectivity. DNS is also a critical element for cybersecurity, as it plays an important role in detecting and blocking malicious activity.
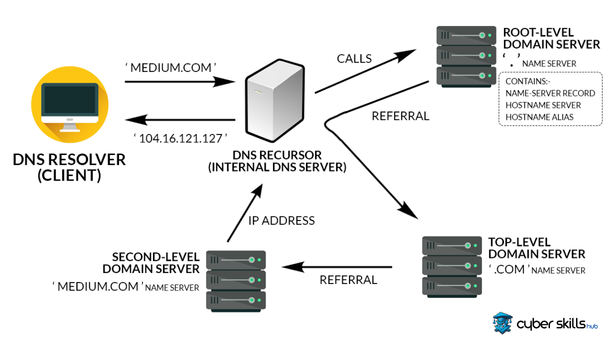
DNS Resolution Process
DNS resolution allows internet users to access any website by translating domain names into IP addresses. This resolution serves as a great guidance service.
When a user enters the name of a website into his or her browser, the local DNS resolver of his or her computer or other network device first receives the query. The local DNS resolver looks for the queried address among previously visited and cached addresses. If this address is not found in the cache, the resolver follows a series of steps to process the query and find the correct IP address.
This series of steps can be processed in two different ways: recursive or iterative DNS queries. In recursive queries, the local DNS resolver makes a series of queries until it resolves the name and returns to the user with the result. With recursive queries, each query is directed to different DNS servers and the results are sent back to the local resolver.
In the final stage, the local DNS resolver gets the final IP address and passes this information to the user’s browser. The browser uses this IP address to connect the user to the website they are looking for. The speed and reliability of the DNS resolution process is vital to the availability and performance of the internet and is essential to the overall security of the network.
DNS Record Types and Importance
DNS records define the relationships between domains and their IP addresses. Thanks to these records, clients on the internet can resolve domains to the correct IP addresses. Users can then access websites using their domain names and the process is transparent.
The most common DNS record type is the A Record, which returns the IPv4 address of a domain. The AAAA Record is used to specify IPv6 addresses. These two record types are taken as the basis for resolving a domain name directly to an IP address.
However, DNS records are not only used to locate IP addresses, but also to associate them with specific services, such as mail servers. The MX (Mail Exchange) Record identifies the address of the e-mail server, while the CNAME (Canonical Name) Record allows a domain name to have an alias and queries to be translated between them.
Beyond that, the TXT (Text) Record supports security mechanisms and defines, for example, Sender Policy Framework (SPF), DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM) and DMARC policies. Proper configuration of these records strengthens domain owners’ protection against cyber attacks such as phishing and spoofing, and also helps recipients to recognize such potential threats. Understanding and correctly configuring DNS record types is therefore critical to the overall security of the network.
Role of DNS in Your Internet Experience
The job of DNS is to make it easy and fast for users to access websites. Without this system, you would have to memorize complex IP addresses to access websites. In short, DNS simplifies your internet experience and allows you to move seamlessly from site to site, providing a user-friendly navigation experience.
DNS, also known as the Address Resolution Protocol, is like the internet’s telephone directory. When you type in the name of a website, DNS converts it into the corresponding IP address, allowing your browser to contact the correct server. This process is invisible, takes place in seconds and forms the cornerstone of your internet experience.
How to Access Websites?
Access to websites is provided through the DNS (Domain Name System). DNS allows users to communicate using the corresponding IP addresses, not site names. This system is sometimes called the “telephone directory of the Internet”.
DNS servers map each domain name to its corresponding IP address. For example, when a user wants to visit”cyberskillshub.com“, the DNS server translates that domain name into an IP address.
This process is called a DNS query. When the user enters a URL in a browser, the computer’s DNS resolver is activated and initiates a query to find the IP of the requested address. This query usually takes place through local DNS servers, a process by which the user’s request is forwarded to the nearest DNS server.
If the local DNS server holds the IP address of the requested domain in its cache, the information is passed directly to the browser. If this information is not in the cache, the DNS query is relayed between a number of DNS servers until the requested information is retrieved. This process is hierarchically organized and may involve multiple layers for efficient resolution. The speed and security of this process directly affects the degree of seamlessness of internet navigation.
Importance of the DNS Query Process
The DNS query process is the foundation of basic internet functionality.
When a user wants to access the internet, they basically perform a DNS query. The DNS query works like the internet’s phone book, returning the quantitative address information of a web address, i.e. the IP address, which allows the user to access the system they want. Thanks to this process, we can browse the internet without having to memorize complex IP addresses.
Without the DNS query process, internet use would not be possible.
An easy user experience – and therefore continued usage – depends on the efficiency and reliability of the DNS query process. Without an efficient DNS querying mechanism, access to the internet can experience severe slowdowns and errors, negatively impacting the user experience.
The DNS query process represents an important aspect of cybersecurity. Vulnerabilities can make it easier for malicious actors to engage in harmful activities. By 2024, DNS security is a priority area for many organizations. Effective DNS query processes and infrastructure need to be continuously improved to prevent security breaches and prevent data leaks.
DNS Settings and Security
DNS configuration is vital for internet usage and plays a critical role in ensuring security. A robust DNS configuration is necessary to protect against malicious actors and attacks such as DNS hijacking or spoofing. Secure DNS usage can be achieved by choosing trusted and authenticated DNS servers, using up-to-date and attack-resistant DNS software, and regularly applying security patches. In addition, enabling security protocols such as DNSSEC (Domain Name System Security Extensions) ensures that data is encrypted and transmitted in integrity, thus providing users with better protection against manipulation of internet traffic.
Choosing Trusted DNS Providers
Choosing a reliable DNS provider is vital to protect both your data privacy and the continuity of your internet experience. The user’s online security is directly related to the reliability of the chosen DNS provider. This is why you should be particularly careful when choosing.
In 2019, a major internet outage demonstrated how important it is to protect DNS infrastructure, especially against malicious activity such as DDoS attacks. A reliable DNS provider must be resilient to attacks and promise continuous uptime. Performance and reliability are decisive factors in choosing a provider.
When assessing the reliability of a DNS provider, it is also necessary to pay attention to how it handles and stores user data. Personal data protection and privacy policies are key to determining whether a provider is trustworthy. Preference should be given to providers that do not record data or keep it to a minimum.
Furthermore, the use of data encryption technologies in DNS query processes is an indication that the provider is trustworthy. Supporting protocols such as DNS over HTTPS (DoH) and DNS over TLS (DoT) is essential for security as well as user privacy. These protocols ensure encrypted transmission of queries and prevent third parties from viewing the data.
The best DNS providers are usually those with a large infrastructure and multiple servers around the world. Server diversity and geographical spread means a service that is both fast and uninterrupted. To ensure that your network is always active, you should choose providers that offer such a robust structure.
DNS Hijacking and Prevention Methods
DNS Hijacking occurs when attackers manipulate a user’s internet traffic to redirect it to unwanted sites. This type of attack has the potential to compromise users’ sensitive information.
Protection is mainly at two levels: Individual users and corporate network administrators. Individual users can improve personal device security by using up-to-date and reliable antivirus software. Corporate network administrators can protect the corporate network by tightening network firewalls and DNS security settings. Encryption of DNS query traffic, frequently updated firewall rules and continuous monitoring are effective barricades against possible DNS Hijacking attempts.
Education and awareness also play an important role. It is important to make users aware of websites and email links that appear legitimate but are actually harmful. Choosing existing and trusted DNS providers over fake DNS services and understanding DNS queries are critical steps in increasing security awareness.
Finally, using updated operating systems and software is a strong line of defense against DNS Hijacking attacks. Software updates close known vulnerabilities and make it harder for hackers to exploit them. Using the secure connection protocols DNS over HTTPS (DoH) and DNS over TLS (DoT) are also effective ways to minimize cyberattacks.
Troubleshooting DNS Problems
When you encounter DNS problems, you should first check your local network settings and the DNS servers of your internet service provider. When a problem is detected, restarting your modem and router can often provide temporary solutions. If these steps do not work, you may alternatively want to consider switching to a different DNS service. Such changes can often resolve access issues and improve the stability of your internet connection.
In some cases, it may be necessary to clear the cache to solve problems caused by outdated or incorrect information in the DNS cache. To accomplish this, different commands are used depending on your operating system; for example, on Windows. In addition, security protocols such as DNSSEC can be enabled to improve security, but it is important that these steps are configured correctly, as misconfigurations can cause new problems. Finally, for unresolved DNS issues, consulting a trusted IT support team is the best approach.
Common DNS Errors and Solutions
DNS errors are often caused by misconfigurations or network connectivity problems. Common errors include “DNS Server Not Responding” or “DNS Address Not Found” messages. When you encounter such situations, you can initially find a solution by following the basic steps.
Workarounds include restarting the modem and router. This can resynchronize network devices and fix many DNA errors.
If a reboot does not solve the problem, a permanent solution is to use a different DNS service. For example, alternatives such as the public DNS services 8.8.8.8.8 (Google) or 1.1.1.1.1 (Cloudflare) can quickly resolve the issue and usually offer faster response times.
The first step in resolving DNS errors is to make a clear and accurate error identification. First, it is important to carefully analyze the error messages and identify the source of the problem. Diagnostic tools such as network tests (ping, tracert, etc.) can be used to determine whether the error is client-side or server-side. For client-side errors, local network settings and cache cleaning can be applied, while server-side problems may require contacting your DNS provider and getting support.
How to Clear DNS Cache
The DNS cache is a local storage area that temporarily stores the IP mappings of the internet addresses you visit. This mechanism, which increases the speed of access to the internet, can cause connection problems when it contains outdated or inaccurate information.
Clearing the cache can help solve these problems. First of all, different steps should be taken depending on your operating system.
In the Windows operating system, the DNS cache can be cleared by running the command ‘'ipconfig /flushdns‘ from the ‘Command Prompt’. This will reset the records and reconfigure the connection.
For macOS users, a similar process is performed by typing ‘sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder‘ into the “Terminal” application. Note that the authorized user password must be entered.
In Linux distributions, the command ‘sudo systemctl restart nscd‘ restarts the name resolution service, which clears the cache. Depending on the distribution, the command may differ.
On mobile devices, clearing the DNS cache is usually done by restarting the device. However, in some cases, especially when operating system details require intervention, it may be necessary to manually clear the DNS cache from the relevant network settings.
Frequently Asked Questions About DNS
What is DNS and how does it work?
DNS (Domain Name System) is like the telephone directory of the internet. It translates domain names that users can easily remember into IP addresses that devices on the internet can understand.
What is the DNS Resolution Process?
When a user enters the website name into their browser, the DNS resolution process begins. In this process, the DNS server translates the domain name into an IP address, which allows the user to access the website.
What Are DNS Record Types and Why Are They Important?
DNS records contain the information necessary for devices on the internet to correctly recognize and communicate with each other. The most commonly used record types include A, AAAA, MX, CNAME and TXT records. These records support operations ranging from accessing websites to forwarding email.
What is the Role of DNS in the Internet Experience?
DNS allows users to access websites quickly and easily. It simplifies and speeds up the internet experience by eliminating the need to remember IP addresses.
How to Choose Reliable DNS Providers?
Performance, security, and privacy policies are important when choosing a reliable DNS provider. Choose providers that offer resilience against attacks and protect user data.
What is DNS Hijacking and How to Avoid It?
DNS Hijacking is when attackers manipulate users’ DNS queries to redirect their traffic to unwanted sites. Using reliable antivirus programs and strengthening network security settings can protect against such attacks.
How to Troubleshoot DNS Problems?
DNS problems can usually be fixed by checking network settings, restarting the modem and router, or switching to a different DNS service. Also, clearing the DNS cache can be a solution.







