Currently Empty: $0.00

It is a complex structure that forms the basis of modern communication systems. This model divides network communication into seven layers, providing a framework for understanding how data transfer occurs. Each layer of the OSI model performs specific tasks, ensuring the smooth transmission of data from one device to another.
In this article, we will examine the details of the OSI model. First, we will cover the basics of the model, followed by a detailed description of its seven layers. Next, we will discuss the advantages and disadvantages of the OSI model. Finally, we will see how the OSI model is used to solve network problems and compare it to the TCP/IP model. This information will help you gain a better understanding of network management and troubleshooting.
Fundamentals of the OSI Model
Definition of OSI Model
The Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model is a very important concept underpinning network communications. This model is critical to understanding how data transfer between networks occurs. The OSI model provides a conceptual framework that standardises the functions of a communication or network system. Basically, it divides network communication into seven layers, and each layer has specific responsibilities to ensure efficient data transmission and interoperability.
The model has a layered structure that defines how data should be transmitted between two endpoints or nodes. Each layer operates independently, but interacts with the layers directly above and below it. This structure allows each layer to perform specific functions while relying on services provided by the layer immediately below it.
History of the OSI Model
Its development started in the late 1970s and early 1980s. The model developed by the International Organization for Standardisation (ISO) was created to facilitate interoperability between different software and hardware systems. The first OSI standards were created by ISO’s TC 97 (Technical Committee 97), Information Processing.
In 1984, ISO published the last OSI standard. This standard includes seven layers: physical layer, data link layer, network layer, transport layer, session layer, presentation layer and application layer. The model quickly gained widespread acceptance and became an important guide for network operations.
Purpose of the OSI Model
Its main purpose is to enable network architectures and protocols to be used as a component of a network product. This model is an industry effort aimed at getting participants in the industry (hosting vendors, ISPs and individuals) to agree on common network standards. Understanding the OSI model is critical as it helps diagnose and troubleshoot network problems.
The model defines how applications running on network-aware devices communicate with each other. This ensures harmonious and efficient communication between different systems. The OSI model is an important tool for gaining a better understanding of network management and troubleshooting. To learn more about network layers and data communication, you can review our Cyber Security Basics Training.
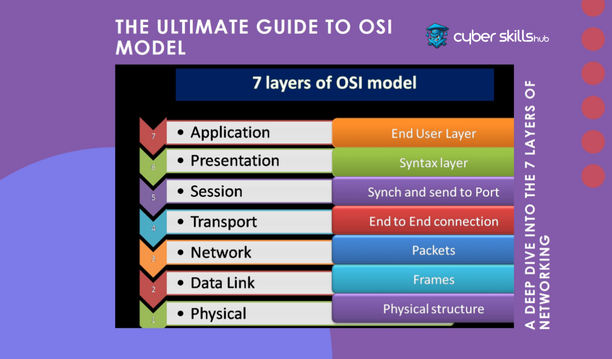
7 Layers of the OSI Model
It standardises network communication by dividing it into seven layers. Each layer performs specific tasks to ensure the smooth transmission of data from one device to another. These layers are ordered from the physical layer to the application layer and each has specific functions.
The 7 layers of the OSI model are:
- Application Layer
- Presentation Layer
- Session Layer
- Transport Layer
- Network Layer
- Data Link Layer
- Physical Layer
Each layer performs specific functions in data transfer and regulates network communication.

Application Layer
The application layer is the top level that enables users to access network resources and perform operations. This layer makes it possible to run applications such as e-mail, file sharing, web browsing. Protocols such as HTTP, FTP, SMTP, DNS operate at this layer. As the layer closest to the user, it converts data into an understandable format.
Presentation Layer
The presentation layer ensures that data is transferred harmoniously between different devices and applications. This layer takes care of the encoding, encryption, compression and character set conversions of the data. For example, when a web page is downloaded to a browser, the presentation layer determines how the data is encoded and interpreted.
Session Layer
The session layer manages the communication between two applications. This layer is responsible for initiating, managing and terminating sessions. It performs operations such as user authentication, authorisation and session control. It also manages the flow of data and communicates with other layers by breaking messages into small pieces.
Transport Layer
The transport layer manages end-to-end communication between devices. It divides the data into segments and reassembles it on the receiving device. Flow control and error management take place at this layer. The TCP and UDP protocols operate at this layer. The transport layer ensures that data is sent at a speed that the receiver can process and controls transmission errors.
Network Layer
The network layer is responsible for the routing and delivery of packets. The IP protocol works at this layer. The network layer enables communication between different networks, determines the optimal path and updates routing tables. It also performs traffic management to meet quality of service (QoS) requirements. For more information about the functioning of network layers and routing of data packets, you can read our article ‘What is NetBIOS and How Does it Work?
Data Link Layer
The data link layer manages data transfer between devices and corrects errors. It divides data into frames, performs error detection and correction, flow control and addressing. It is divided into two sublayers, MAC and LLC. This layer ensures that data is transmitted to the correct device using physical addresses (MAC addresses).
Physical Layer
The physical layer is the lowest layer. It forms the physical connection that allows data bits to be transferred from one device to another. Cables, connectors, data transfer rates and data marking methods are of interest to this layer. The physical layer prevents signal attenuation, corrects data errors and ensures data integrity.
Advantages and Disadvantages of the OSI Model
Advantages of the OSI Model
It offers many advantages in network communication. Firstly, this model allows us to see the big picture of data communication over the network. Since each layer performs a specific job, it can be considered and tested separately. This feature facilitates the troubleshooting process and allows network administrators to identify the source of problems faster.
It can be used to compare the basic functional relationships in different networks, showing how hardware and software work together. This helps network designers and managers develop a better understanding between different systems.
The abstraction provided by the model allows us to modify any layer without affecting other layers. This feature allows new technologies to be easily integrated and increases the flexibility of network systems.
Disadvantages of the OSI Model
There are also some disadvantages. For example, some services provided by the various layers are duplicated. Functions such as flow control and error checking can be performed in multiple layers, which can lead to inefficiencies.
The model can be quite complex, slow and costly to implement and use. This can be a disadvantage, especially for small-scale networks. It is theoretical in nature and may not be fully adequate for practical data transmission and communication. Therefore, some limitations may be encountered in real world applications.
OSI vs TCP/IP Comparison
There are important differences between the OSI model and the TCP/IP model. TCP/IP has a simpler structure than the OSI model and compresses several OSI layers into a single layer. For example, layers 5, 6 and 7 of OSI are combined into a single Application Layer in TCP/IP.
TCP/IP is a functional model designed to solve specific communication problems, while OSI is a generic, protocol-independent model designed to describe all forms of network communication. For this reason, TCP/IP is more practical and widely used, while OSI is used more as a reference model.
Whereas in the OSI model each layer has a clearly defined function, in the TCP/IP model the functions between layers are more tightly integrated. This makes TCP/IP more flexible and adaptable.
In conclusion, both models are important tools for understanding and managing network communications. While the OSI model provides a detailed theoretical framework, TCP/IP offers a more practical and widely used approach.
Conclusion
It is a seven-layer structure that forms the basis of network communication. This model provides a framework for understanding and managing data transfer. Each layer ensures the smooth transmission of data by performing specific tasks. Understanding the OSI model helps network administrators diagnose and solve problems.
In conclusion, the OSI model has an important place in network communication. The advantages and disadvantages of the model provide a basis for comparing it with other models such as TCP/IP. This information helps us to make better decisions in network design and management. Understanding the OSI model is important for solving the complex structure of modern communication systems.
Frequently Asked Questions About OSI Model
What is the OSI Model and Why is it Important?
The OSI model (Open Systems Interconnection) is a reference model used to understand how data is transmitted in network communications. This model divides data communication into seven layers, allowing each layer to perform specific tasks. It plays a critical role in solving network problems, ensuring compatibility between different networks, and understanding communication protocols.
What is the Difference Between OSI Model and TCP/IP Model?
While the OSI model is more abstract and theoretical, the TCP/IP model is a more practical and widely used protocol set. TCP/IP consists of 4 layers, combining some of the 7 layers of OSI: Application, Transport, Internet and Network Access. The OSI model provides a more detailed reference, while the TCP/IP model is more suitable for real world applications.







