Currently Empty: $0.00

Once upon a time, libraries were seas of knowledge and shelves were islands of information.
The librarian’s guidance is like a compass in that sea; APIs are the compasses that guide users through this sea of information in the digital world.
Today, when you open a weather app on your phone, it doesn’t just display local weather data; it queries vast data networks on remote servers through APIs and provides you with instant information.
APIs are bridges in this sense.
API Basic Definition
API (Application Programming Interface) is an interface that allows applications to interact with each other and with other services. It makes it possible to easily share and integrate different software, data and functions. So, for example, a mapping service can share location and route information with another application in a secure and organized way.
Through these interfaces, application developers gain quick access to existing data and services, opening the door to building more complex and functional applications. APIs are critical to avoid code duplication and speed up the software development process.
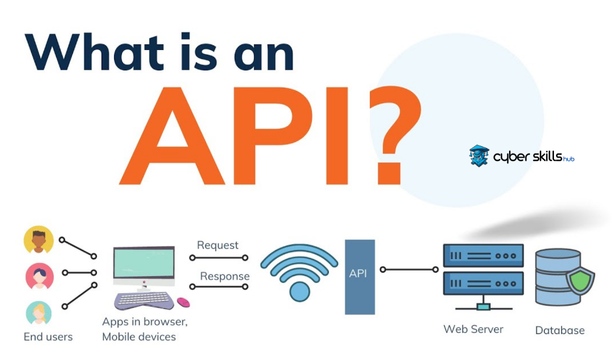
How does the API Work?
The API acts as an intermediary between servers; it organizes the exchange of data between the client and the server. A request made by the user is transmitted to the server through the API. It provides data flow within the framework of specific security protocols and data formats, thus enabling reliable communication.
For example, your location query in a mapping application is converted into an API request by the application and sent to the relevant server. The server makes the necessary query in the database and sends the requested location information back to the application via API. The process is usually performed using standard data structure formats such as JSON or XML.
APIs are the digital diplomats that enable millions of devices and applications to communicate instantaneously.
For a successful API operation: First, the API client specifies the metadata of the request (method type, request information, etc.), then the request is sent over the HTTP protocol. The server evaluates the request from the API, generates an appropriate response and sends it back in the same way. The speed and security of the server play a critical role in the efficiency of this process.
Different Types of API
APIs are divided into several categories according to their structure, and each type is better suited for specific tasks. The most common are web APIs, which enable communication with services on the Internet.
For example, REST (Representational State Transfer) APIs work transparently over the underlying protocols of the internet and are therefore very popular. The fact that they have a stateless architecture, i.e. they do not store state information, makes this type of API scalable and flexible. Another type is SOAP (Simple Object Access Protocol) APIs, which have stricter standards and offer additional security features.
A different approach is GraphQL APIs. They allow developers to make more detailed queries on data schemas, allowing them to retrieve data according to their needs and increase efficiency. This provides the advantage of optimizing data bandwidth and performance, especially for mobile applications.
Finally, WebSocket APIs are used in situations where real-time data transfer is required. It establishes a two-way communication channel and, accordingly, is ideal for situations where a continuous flow of data is required. For example, the use of WebSocket APIs is common in scenarios such as instant messaging or streaming live price data. These APIs provide an effective solution for time-sensitive applications.
Benefits of API
APIs increase the flexibility of the system and facilitate integration between different platforms. This enables modularity and reusability in software development. Acting as a standard interface for data sharing, APIs allow different applications and services to interact with each other. Especially in microservice architectures, APIs are critical for independent services to work together.
For real-world problem solving, off-the-shelf APIs are preferred over customized solutions, speeding up development processes and reducing costs. In addition, APIs enable centralized updating and management of data, which significantly improves data consistency and security. In terms of security, APIs can be equipped with layers such as access control and data authentication mechanisms, providing effective protection against unauthorized use.
APIs enable the development of innovative applications, enriching the user experience and enabling more interactive services. For businesses, APIs play a central role in collecting and processing valuable information in areas such as data analytics and business intelligence, supporting decision-making processes.
Increasing Efficiency
APIs greatly increase development efficiency by providing modularity and flexibility in software development. Using standardized interfaces, different components can easily integrate with each other, speeding up the development process.
Furthermore, API integration simplifies the process of scaling applications. This is vital for responding quickly to high demands and supports more efficient use of system resources.
The reusability offered by APIs simplifies the processes of inter-system connectivity and data exchange, allowing developers to build on existing code bases and add new functionality. This saves both time and money and helps bring projects to market more quickly.
By providing a clearer division of labor between members of the development team and allowing each part to be tested individually, API integrations contribute to reducing software defects and improving the overall quality of the application. This also enables quality assurance processes such as unit tests and integration tests to be managed more effectively, thereby increasing the reliability of the software.
Ease of Integration
APIs enable seamless integration between multiple systems and applications, giving developers the flexibility to adapt across many different platforms and languages. This means that the API acts as a bridge across technological diversity.
Incompatibility issues that are often encountered during the integration phase are minimized thanks to APIs. APIs communicate using standard protocols.
Moreover, enabling data flow between different applications enables innovations to be introduced without disrupting well-established systems. Innovations can be easily integrated without disrupting existing structures.
Using API integrations, organizations can add new features and services while protecting their investments. This is critical for them to remain dynamic and adaptable in a competitive market.
Without the need to extend or replace the existing system, APIs can quickly integrate into existing infrastructure, allowing businesses to evolve rapidly. APIs that adapt to existing systems are the cornerstone for building evolvable structures.
In short, the integration process becomes easier and more flexible with the use of APIs, making it possible for systems to operate more efficiently, saving time and cost. APIs play an important role in the modernization and automation of business processes.
API Usage Scenarios
APIs enable secure and efficient data exchange between applications. For example, social media platforms make integrations that allow users to share content.
E-commerce sites bring together APIs from different services to manage customer orders and track cargo. In this way, the entire process from order placement to delivery can be managed on a single platform, reducing workload.
Mobile apps analyze user data with APIs running in the background and deliver personalized experiences. This increases app usability and engagement.
Communication between Applications
An API is the ability for applications to talk to each other.
The most prominent feature of modern software architectures is the ability to integrate various applications with each other in terms of data and functionality. The technology that makes this integration possible is defined as Application Programming Interfaces (APIs). With APIs, one application can take advantage of functionality or data provided by another application.
APIs connect applications written with different technologies.
This allows systems to communicate harmoniously with each other in a platform-independent way – that is, one system can run on Windows while another can run on Linux. With the proliferation of APIs, the flexibility and speed of communication between applications has increased dramatically.
APIs improve workflows through efficient system integration.
For example, a payment system API can be integrated into an e-commerce site, allowing customers to pay securely. In this transaction, the API enables critical information such as card details and payment confirmation to be securely shared with the relevant payment service provider. APIs are therefore critical for data security and transaction transparency.
Big Data and Analytics
Big data refers to the abundance of complex data that organizations face today and offers high value to analyze. Analytics processes require specialized tools and methodologies to extract insights from large data sets.
- Data Mining: Discovering patterns and relationships from large data sets.
- Machine Learning: The use of automated model building and learning algorithms in data analysis.
- Real-Time Processing: Analyzing and translating instantaneous data streams into action.
- Forecast Analysis: The prediction of future events or trends.
The analysis of big data guides organizations in making better decisions and developing strategies.
Big data analytics is an ecosystem that is constantly fed through APIs, and cybersecurity skills are critical to protecting it.
API Tasarım ve Güvenlik İlkeleri
In the process of designing and developing APIs, it is essential to consider security principles as a fundamental building block. A properly designed API should include access control appropriate to authorization levels, integrate data authentication and encryption mechanisms, and have reliable error response strategies. In essence, API design should include security protocols to ensure that only authorized users and systems can interact between the client and the serverAPI Design and Security Principles.
Advanced API security approaches recommend layered defenses supported by frameworks. Authorization using standards such as OAuth, OpenID Connect and JWT (JSON Web Tokens) should be combined with advanced data protection methods. Furthermore, continuous monitoring and regular security audits are vital to maintain the security of an API. Every API request needs to be logged and suspicious activity needs to be detected in a timely manner so that the system can remain resilient against potential cyber-attacks.
RESTful API Design
RESTful API design serves a specific situation and performance requirements by adopting a resource-based structure. This structure aims to establish an efficient communication between client and server and allows resources to be represented over web protocols.
Resources are identified via URL and interact with HTTP methods.
REST architecture should be stateless and work independently between each request. This feature offers significant advantages in system scalability and multi-client support.
RESTful APIs typically use lightweight data formats such as JSON or XML. These formats express data in a machine- and human-readable way, while enabling efficient data flow over the network.
The correct use of HTTP methods (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE) has an important role in RESTful API design. Each method represents specific operations on resources and standardizes the behavior and interaction of the API.
Finally, the HATEOAS (Hypermedia as the Engine of Application State) principle is also important in REST API design. This involves hypertext or hyperstructures that the client can explore and interact with, thus dynamically allowing users to navigate between different resources.
How to Secure the API?
Securing APIs is vital for cybersecurity professionals and requires a careful approach.
- Advanced Authentication and Authorization Mechanisms: Strong authentication methods ensure that the API is protected against unauthorized access. Authorizing API access with token-based systems such as OAuth, JWT are the most common methods.
- Data Encryption: Data must be encrypted both in transit (using TLS/SSL) and in storage (e.g. in databases).
- Access Controls: Detailed access controls should be set up so that users and systems can access only as much information as necessary.
- Penetration Prevention and Detective Controls: Potential threats should be identified by monitoring, logging and regular security analysis against attacks.
- Error Management: It is important that errors are managed correctly and sensitive information is not leaked through error messages.
- Limiting and Rate Limits (Rate Limiting): It is useful to set request limits and rate limits to prevent overuse of the API.
- Updates and Patch Management: Regular API updates and patches are a critical step to close known vulnerabilities.
Authentication and encryption are the two cornerstones of security.
API security should be a continuous process to protect system integrity and the confidentiality of user data. Securing APIs also brings cybersecurity skills to the forefront. Those who want to gain the necessary cybersecurity knowledge to understand and prevent API vulnerabilities can attend the “Cybersecurity Fundamentals Training” course offered through the “Cyber Skills Hub”. This course will help you improve your skills in this area by providing in-depth knowledge on API security. To learn more about the course, you can visit the Cyber Skills Hub website.
Frequently Asked Questions About API
What is an API?
API (Application Programming Interface) is an interface used for applications to interact with each other and with other services. This makes it possible to easily share and integrate data and functions between different software.
How do APIs work?
APIs organize the exchange of data by acting as an intermediary between the client and the server. User requests are transmitted to the server through specific security protocols and data formats, and the processed data is returned through the API.
What are the types of APIs?
The most common API types include REST, SOAP, GraphQL and WebSocket. REST APIs are popular for their stateless nature, SOAP prioritizes security, GraphQL provides flexible queries and WebSocket is used for real-time data transfer.
What are the benefits of API?
APIs increase efficiency, facilitate integration between different platforms and enable modular software development. They are also critical for the interoperability of independent services in microservice architectures.
What are the API use cases?
APIs are used in various areas such as content sharing on social media platforms, order and shipping management on e-commerce sites, and personalized experiences in mobile apps. They are also important for securely and efficiently exchanging data between applications.
How to ensure API security?
API security is ensured by strong authentication methods, data encryption, access controls, intrusion prevention and detective controls. Regular security audits and updates also support security.







