Currently Empty: $0.00

In the digital age, data has become the most valuable asset.
Information security refers to the steps taken by individuals and organizations to protect data, the greatest wealth of this age. These steps include technical, operational and administrative measures to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access, disclosure, alteration and destruction. The ever-increasing cyber threats increase the importance of information security.
Information Security Fundamentals
Information security is built on the principles of confidentiality, integrity and availability. These three fundamental principles play a vital role in protecting data and increasing resilience against cyber-attacks.
To develop an effective information security strategy, whether at the organizational or individual level, it is essential to invest in risk assessment and management processes. This includes analyzing threats and vulnerabilities, selecting and implementing appropriate security controls.
Continuous training and awareness raising are the cornerstones of information security. Knowledge of current threats and defense mechanisms is the basis for developing a proactive approach to security vulnerabilities.
Definition of Information Security
Information security refers to the protection of individual and corporate data against unauthorized use, disclosure, modification and destruction. Basically, the purpose of this protection is to ensure security integrity.
Information security, which is closely related to cyber security, includes three basic principles: ensuring data confidentiality, protecting data integrity and maintaining data accessibility. These principles form the basic structure of security.
In information wars, the most valuable resource is properly protected data.
Especially in today’s world where digital transformation is accelerating, information security plays a critical role in combating advanced cyber attacks, preventing data leaks and maintaining business continuity. It has become a strategic investment area for organizations.
Basic Terms and Concepts
There are basic terms and concepts that individuals who will specialize in the field of information security must master.
- Confidentiality: The principle of preventing unauthorized persons from accessing sensitive information.
- Integrity: Refers to the protection of data against unauthorized or unauthorized changes.
- Availability: Ensures that systems and data are accessible when needed by authorized users.
- Risk Management: The process of identifying, assessing and taking measures against potential security threats.
- Encryption: The process of making sensitive data unreadable against unauthorized access.
- Authentication: The process of verifying the identity of users.
- Authorization: The management of verified users’ access permissions to specific resources.
These terms form the cornerstones of cybersecurity strategies and enable experts to identify threats in these areas and develop effective defense mechanisms.
In the information security process, in addition to these concepts, it is necessary to have in-depth knowledge of attack types, defense methods, security policies and legal regulations. In this way, security professionals can effectively manage risk and optimize security measures.
For a deeper understanding of the basic principles of cybersecurity, see ourarticle ‘Social Engineering Attacks:Protection Methods‘ for a deeper understanding of the basic principles of cybersecurity. This content discusses in detail the definition of cyber threats and the measures that can be taken against them.
Cyber Threats and Ways of Protection
Cyber threats can be defined as a variety of malicious activities, including various types of attacks such as malware, identity theft, phishing and ransomware. These attacks can put the data, reputation and financial resources of companies and individuals at risk. A comprehensive security approach and constantly updated defense strategies are vital to preventing these threats.
The main ways of protection include using strong and regularly changed passwords, implementing two-factor authentication and protecting systems with up to date antivirus software. These measures serve as the first line of defense against cyberattacks and help minimize potential breaches.
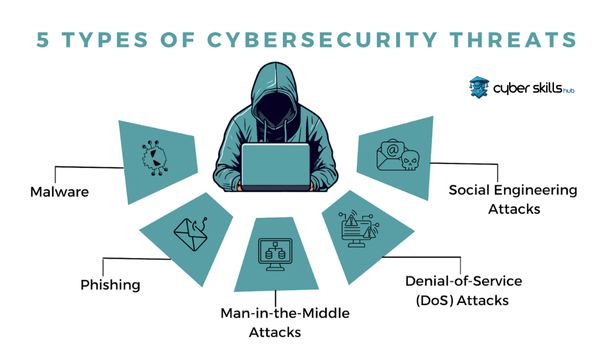
Common Cyber Threats Today
In the field of cyber security, the threat manifests itself in many different forms. Covert attacks, called Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs), which can last for months or even years, are carried out by organized criminal groups and systematically penetrate the firewalls of organizations. APT attacks are used for long-term intelligence gathering and data breaches, so they must be considered at all times.
Ransomware attacks encrypt data and demand a ransom. This threat’s ability to spread rapidly and its complex encryption algorithms make it particularly dangerous. Ransomware can severely undermine the operational capabilities of organizations and cause significant financial losses.
Phishing attacks use social engineering tactics to redirect users to seemingly legitimate but malicious websites and attempt to capture their personal information. This type of attack usually occurs through emails, social media messages or online advertisements. Current events or popular topics are taken into account to attract the attention and gain the trust of targeted individuals.
Finally, Insider Threats pose a serious risk to organizations. This is when insiders or collaborators intentionally or unintentionally cause harm. Insider threats can leak organizations’ sensitive data, gain unauthorized access to systems and damage IT infrastructure. Therefore, regular security training and an effective internal audit system should be an integral part of a cybersecurity strategy.
Effective Prevention Strategies
The first step in protecting against cyber-attacks is to establish and continuously update a strong security policy. Security protocols need to evolve in parallel with the technology used. Companies and individuals should conduct risk assessments and identify their critical assets so that they can take the necessary measures to protect them.
Firewalls and antivirus programs are essential security components. These tools play a major role in preventing malware from infiltrating the system by detecting threats at an early stage. A firewall monitors external network traffic, while antivirus software scans for malicious files and code. Moreover, creating strong boundaries between specific network segments protects against internal attacks.
Up-to-date security patches and software updates close vulnerabilities in systems, preventing them from being exploited by cyber attackers. Each software update offers the chance to address potential vulnerabilities, so regular updates should be made. The use of strong and complex passwords significantly reduces unauthorized access to accounts. Password managers and two-factor authentication systems are more effective than a layered security approach and should be adopted.
Increasing network detection and response capabilities is vital to be able to act quickly in the event of a breach. Intrusion detection systems (IDS) and intrusion prevention systems (IPS) offer proactive protection against cyber threats. With these systems, abnormal network traffic or suspicious activity can be immediately detected and responded to appropriately. These processes should be supported by continuous monitoring and analysis of log records.
Education and awareness programs strengthen the human factor, which is often the weakest link in cybersecurity protection. Making users aware of social engineering attacks such as phishing and not clicking on misleading links can prevent human-caused security breaches. Regular training sessions and simulation tests increase preparedness against potential threats.
Most importantly, encryption of data plays a critical role in protecting sensitive information from unauthorized access. Encryption is used to ensure the integrity and confidentiality of data and prevents information from being understood and used even if it is leaked. Addressing all these strategies within a holistic cybersecurity framework ensures effective protection.
Encryption and User Authentication
Encryption is an indispensable method for protecting sensitive data against unauthorized access. By using various algorithms, data is made secret so that unauthorized persons cannot read it. Keys accessible to the data owner and authorized users play an important role in this process. Strong encryption methods keep users’ personal information secure, for example financial data or sensitive communications.
User authentication is another critical security element that regulates access to certain resources. Authentication mechanisms include passwords, two-factor authentication (2FA) and biometrics. Passwords are the first and most common line of defense for security, but they can be insufficient on their own. Therefore, taking additional measures such as 2FA alongside passwords means protecting user identities in a multi-dimensional way. Two-factor authentication helps strengthen weak points within firewalls and provides an extra layer of protection against cyber-attacks.
Importance of Encryption
Encryption is vital for protecting data in the digital environment, as advanced encryption techniques allow data to be stored securely against unauthorized access. This is particularly important when communicating sensitive data and ensures that data integrity is maintained.
Encrypting data also prevents data misuse. Preventing the leakage of sensitive information is possible with encryption.
Especially in sectors where the risk of data leakage is high, encryption is a key security measure. Financial sectors such as banking and healthcare are important areas where encryption is used.
Encryption algorithms should be continuously developed and updated against changing threats. At this point, it is essential to select and implement algorithms that are strong enough to be effective against emerging cyber threats.
Encrypting data not only protects the confidentiality of that data, but also guarantees that a completed transaction cannot be altered (non-repudiation). This is particularly important in legal and financial transactions.
Finally, encryption standards should be continuously reviewed and improved to enhance the security of users. Effective encryption strategies form the basis for a proactive approach to threats.

Tips for Creating a Strong Password
A strong password is one of the most important lines of defense in cybersecurity. In an expert security approach, simple and predictable passwords should never be chosen.
The strength of a password is directly proportional to its richness of combinations and unpredictability. In this context, using complex and long passwords makes it harder for cyber attackers. First of all, it is important to choose a password that is at least 12 characters long and should include alphanumeric characters as well as special characters. Strong password policies not only prevent weak combinations of letters or numbers, but also emphasize complexity to maximize security.
Another important factor that should always be kept up to date is not to reuse passwords. A security risk in one account can put all accounts at risk if the same password is used for other accounts. Therefore, creating unique passwords for each platform and account will solidify your cybersecurity from the ground up.
Finally, using password manager software is an effective way to create and manage strong passwords. By securely storing passwords that can be forgotten or lost over time, you can set unique and complex passwords for each login process. You can also minimize the risks of identity theft and unauthorized access by implementing additional security measures such as two-factor authentication (2FA). In this way, you can balance both security and usability under a strong password policy.
For more information on the importance of encryption and techniques for creating strong passwords, see ‘Encryption Techniques:Secure Your Data‘ article. This resource details encryption as a key element of data security.
Information Security Practices for Companies
The first step in ensuring information security at the corporate level is to identify potential threats and security vulnerabilities by conducting a risk analysis. The strategy created as a result of this analysis is the basis for determining and implementing appropriate security policies. In particular, it is critical to integrate technologies such as advanced encryption methods, access control systems and network security solutions to ensure the protection of sensitive data.
In addition, it is important to train employees on cybersecurity and increase their level of awareness. Periodic trainings and tests on cyber security practices should be organized to reduce the risks posed by the human factor. Regular review and adaptation of internal policies to adapt to current threats also play a vital role in ensuring continuity.
Corporate Information Security Policies
Corporate information security policies are the basic document that regulates the processes of managing, protecting and mitigating the risks of a company’s information assets. These policies provide a systematic framework by setting security standards and procedures.
Widely accepted standards such as ISO 27001 and NIST can provide guidance in drafting security policies. Policies cover data classification, access control, encryption, physical security, incident response and business continuity. Each security measure should be tailored to the specific threats and risk profile of the organization and updated regularly.
The creation and updating of policy documents should be an initiative supported by management. This provides the necessary environment for policies to be integrated into the corporate culture and adopted by all employees. Measuring and continuously improving the effectiveness of corporate policies is possible through safety audits and regular training programs.
Finally, compliance and audit requirements are mandatory elements of corporate security policies. To ensure compliance with local and international regulations and industry standards and prevent security breaches, policies must be reviewed and updated quickly when necessary. This is a critical step in protecting corporate reputation and preventing potential legal sanctions. For more detailed information on corporate information security policies and practices, visit our article ‘Cyber Security: How to Defend Against Technological Threats’. This content addresses how companies can protect themselves against cyber threats.
Employee Awareness and Training
The foundation of an organization’s approach to security is informed and trained employees. Regularly informing employees about security policies and procedures helps to proactively prevent security vulnerabilities.
One of the key elements of a successful security strategy is to provide hands-on training through realistic scenarios in which employees take part. This is especially crucial to raise awareness of social engineering attacks and ensure that employees recognize the threats they may face and react appropriately. Security training programs are expected to be effective in both meeting legal obligations and strengthening the organization’s defenses.
In today’s world, where cyber threats are constantly evolving, trainings should be shaped according to current threats. For example, response methods and protection techniques appropriate to the ever-changing threat landscape, such as ransomware and data leakage, should be regularly communicated to employees. This is part of an effective risk management process.
Finally, employees need to be encouraged to report and respond to perceived security breaches. The availability of an effective communication channel and the importance of properly handling a security breach should be emphasized. Trainings that underline the transparency and ease of implementation of these processes are vital for the adoption of a cybersecurity culture throughout the organization.
Join our trainings to learn more about information security and become a cybersecurity expert. Improve your skills in information security with comprehensive content presented by our expert trainers. Step into a secure future with our certified trainings.
Click here for detailed information and registration.
Frequently Asked Questions on Information Security
What is Information Security?
Information security refers to the measures taken by organizations and individuals to protect their data from threats such as unauthorized use, disclosure, modification and destruction. This protection is carried out to ensure the confidentiality, integrity and accessibility of data.
What are the Basic Principles of Information Security?
The basic principles of information security are confidentiality, integrity and availability. Confidentiality ensures that sensitive information is not disclosed to unauthorized persons; integrity ensures that data is protected from unauthorized modification; and accessibility ensures that authorized users can access data when needed.
What Are Cyber Threats and How to Protect Against Them?
Cyber threats come in the form of malicious activity such as malware, phishing, ransomware and can put data, reputation or financial resources at risk. Protection includes using strong passwords, two-factor authentication and up-to-date antivirus programs.
Why Encryption is Important
Encryption protects sensitive data from unauthorized access. It is a critical method to ensure data integrity and confidentiality, especially in industries such as finance and healthcare. Advanced encryption techniques ensure that data is stored securely.
What is Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) and How Does It Work?
Two-factor authentication (2FA) requires two separate layers of security to confirm a user’s identity. It is usually accomplished with a password and a code from a device specific to the user. This method strengthens firewalls and provides extra protection against cyber attacks.
How to Create Corporate Information Security Policies?
Corporate information security policies can be established using standards such as ISO 27001 and NIST. These policies include topics such as data classification, access control, encryption and incident response and should be updated regularly.
Why is Employee Awareness and Training Important?
Employee awareness and training reduces human error in cybersecurity and provides proactive protection. Regular trainings and simulation tests make employees aware of current threats and enable them to react effectively.







