Currently Empty: $0.00
Linux Commands: A Beginner to Advanced Mastering Guide

Linux Command Line Basics
Linux, as a powerful and flexible operating system, offers its users almost unlimited control through the command line. This guide will help you understand the basics of the Linux command line and use it efficiently.
Discover the Power of the Terminal
In Linux, a terminal is an interface that users use to manage their system. It provides access to the heart of the operating system and offers a faster and more efficient experience compared to graphical user interfaces. Terminal offers an interactive experience by typing commands and instantly observing the results.
Basic Commands and Usage
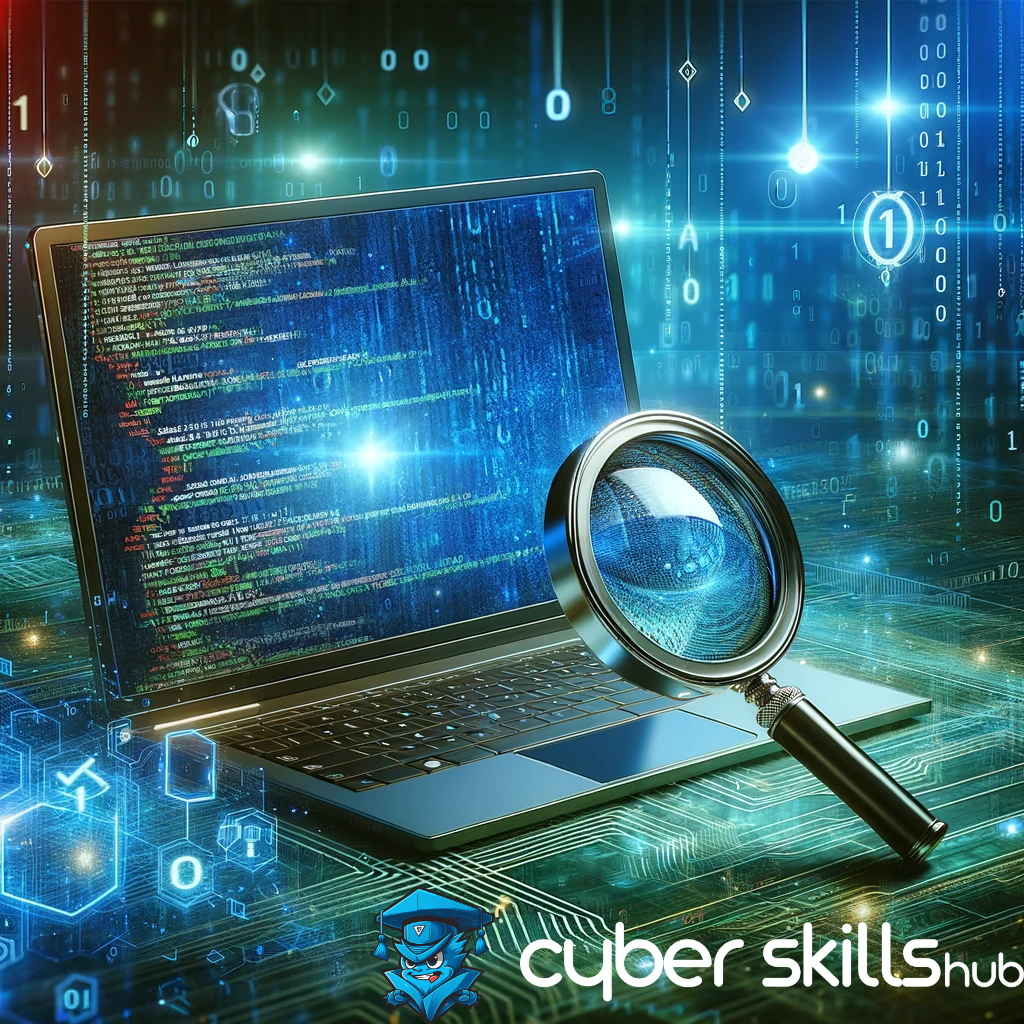
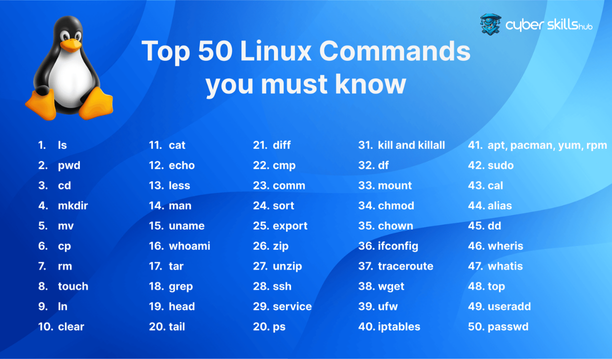
Learning some basic commands is essential to succeed in Linux. Here are some important commands to get you started:
-
ls(list): Lists files and directories in the current directory. -
cd(change directory): Allows you to change to a different directory. -
pwd(print working directory): Shows the full path to the current working directory. -
mkdir(make directory): Creates a new directory. -
rmdir(remove directory): Removes an empty directory. touch: Creates a new empty file or updates the timestamp of an existing file.-
cp(copy): Copies files and directories. -
mv(move): Moves or renames files or directories. -
rm(remove): Deletes files or directories.
Each of these commands comes with various options and parameters to extend their functionality.
File Management Commands
File management in Linux is a fundamental part of everyday work. Here are some common file management commands:
grep: Searches text in files.find: Used to find files and directories.nano,vi,emacs: Different text editors.cat: Displays or merges file contents.chmod: Changes file permissions.chown: Changes file ownership.
These commands are the cornerstones for working effectively on a Linux system. Each of them offers a variety of functions and options to streamline your workflow and increase your productivity.
Methods to Increase Productivity
Mastering Linux is not only about learning basic commands, but also about knowing how to optimize your workflow. In this chapter, we will focus on creating shell scripts and defining command aliases, two key ways to speed up your work and increase your productivity.
Creating Shell Scripts
Shell scripts allow Linux users to automate sequences of commands that they constantly repeat. These scripts are simple text files containing sequential commands and can be executed with a single command. Here are some advantages of shell scripts:
- Automate Repetitive Tasks: Saves time by automating common tasks.
- Error Rate Reduction: Reduces manual input errors.
- Simplify Complex Operations: Simplifies complex operations by combining multiple commands together.
Considerations when creating shell scripts:
- Script Permissions: Scripts must have the appropriate permissions to be executable (
chmod +x script.sh). - Good Commenting: Add comment lines to make the code readable and understandable.
- Debugging Test your scripts and don’t forget to debug them.
Defining Command Aliases
Command alias is a way of replacing long or complex Linux commands with short and easy-to-remember shortcuts. This allows you to run frequently used commands quickly. Examples:
alias ll='ls -alF': Shortens the command ‘ls -alF’ to ‘ll’.alias rm='rm -i': adds an interactive feature to the ‘rm’ command so that deletion requires confirmation.
Aliases are added to shell configuration files such as .bashrc or .zshrc. To define aliases, follow these steps:
- Open your configuration file (
nano ~/.bashrc). - Add the Alias command (
alias name='command'). - Save and close the file and restart your shell or use the
source ~/.bashrccommand for the changes to take effect.
These methods will make you faster and more efficient when using the Linux command line. Shell scripts and aliases will help you simplify challenging tasks and speed up your daily workflow.
System Management and Monitoring
Management and monitoring of the Linux operating system is vital to optimize system performance and detect potential problems early. In this section, we will focus on examining two key areas for system management and monitoring: process management commands and system logs.
Process Management Commands
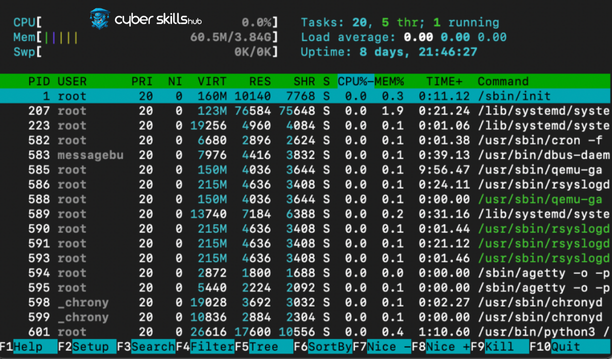
Process management in Linux ensures efficient use of system resources and optimizes performance. Here are some basic process management commands:
top: Shows the processes running on the system in real time. It allows you to monitor important metrics such as CPU and memory utilization.ps: Provides information about active processes. With its various options, you can get detailed information about specific processes.kill: Used to terminate a specific process. With the Process ID (PID) you can safely terminate the process.htop: is an advanced version oftop. It offers a more user-friendly interface and extra features.
These commands allow you to understand how system resources are being used and intervene when necessary.
Reviewing System Logs
System logs keep track of everything that happens in Linux and play a critical role in diagnosing potential problems. Here are some commands you can use to examine the system logs:
journalctl: Provides access to system logs managed by Systemd. You can search logs by timestamps, service names and other filtering options.dmesg: Shows messages recorded during system startup or when there are significant changes at kernel level. Useful for diagnosing hardware and driver problems.-
tail -f /var/log/syslog(on Debian-based systems) ortail -f /var/log/messages(on Red Hat-based systems): Allows you to keep track of log files in real time.
These commands help you effectively review system logs and quickly identify potential problems. Since system logs cover everything from network connections to service failures, checking them regularly is important for healthy system management.
Network Management and Security
Effective network management and security in Linux keeps your systems healthy and secure. In this section, we will cover some basic commands for network configuration, monitoring and security.
Network Configuration and Monitoring
Here are some basic commands you can use to manage and monitor network configuration on Linux systems:
-
ifconfig/ip: Used to configure and display network interfaces.ifconfigis an old command and has been replaced byipon modern systems. netstat: Shows network connections, listening ports, routing tables and network interface statistics.ping: Used to test the status of the network connection. It checks the accessibility of the network by sending packets to a server or IP address.traceroute: Shows the path of packets until they reach their destination, helping to diagnose network problems.
Security and Permits
Security in Linux is one of the most important aspects of system administration. Commands related to file permissions and security include
chmod: Changes file and directory permissions. Used to control users’ access levels to files.chown: Changes the ownership of a file or directory.iptables: A powerful firewall tool. It is used to control and manage incoming and outgoing traffic.ssh: Used to securely connect to remote servers. It provides encrypted data transfer and enables remote administration.
Conclusion
The Linux command line is a powerful and flexible tool. From basic commands to advanced system administration, it is important to understand and use these commands correctly to work effectively in Linux. This guide provides basic information about Linux commands and helps users manage their systems more effectively. Whether you are a novice user or an experienced system administrator, these commands will simplify your daily workflow and increase your productivity on Linux. Armed with this knowledge, you can fully explore the possibilities of the Linux command line and maximize the potential of your system.
If you want to gain more knowledge and skills on Linux command line and bash scripting, you can also check out more learning resources such as Cybersecurity Basics Tutorial. These types of courses provide the basics of cybersecurity and help you improve your technology and security skills.
Frequently Asked Questions about Linux Commands
What is the Linux command line and why is it important?
The Linux command line allows you to operate on the operating system by directly typing commands. This provides faster and more detailed control than visual interfaces, which is why it is indispensable for system administrators and developers.
What are the file management commands in Linux?
Among the basic commands for file management in Linux ls, cd, pwd, mkdir, rmdir, touch, cp, mv, rm commands, such as “File”. These commands are used to list files, change directories, create files and copy or move files.
How to use shell scripts?
Shell scripts allow you to automate and execute multiple commands together. Scripts speed up repetitive tasks, reduce errors and simplify complex operations. Scripts must have the appropriate permissions to be executable.
How to define command aliases in Linux and what are their benefits?
Command aliases are used to make long or complex commands short and easy to remember. For example, the alias ll='ls -alF' definition shortens the command ls -alF to ll. This provides quick access to frequently used commands and improves efficiency.
How to analyze system logs in Linux?
Commands such as journalctl, dmesg, and tail are used to examine system logs. These commands help you to monitor system events in detail and diagnose potential problems.
What are Linux network management commands?
Commands such as ifconfig, ip, netstat, ping, and traceroute are used for network management in Linux. These commands are used to view network configurations, control network connections and monitor routes on the network.
How to manage file and directory permissions in Linux?
chmod and chown commands are used to manage file and directory permissions. You can change file access permissions with chmod and file ownership with chown. These commands are important to maintain system security and control file access.







