Currently Empty: $0.00

Cyber security incidents have become inevitable. The scale of threats is increasing day by day, especially for businesses and many other organizations.
Being prepared for incidents and managing them effectively is crucial. Incident Response is a strategic approach that enables organizations to respond quickly and consistently, especially when a potential security breach occurs. Experts emphasize that this process is a complex structure that includes planning, detection, analysis, response, and recovery stages.
Incident Response Definition
Incident Response is a management process developed to identify, investigate, and eliminate threats to systems and networks in the event of a corporate security breach. This process encompasses proactive and reactive activities in response to information security incidents and aims to minimize risk quickly in line with the organization’s objectives, while reducing the impact of the incident and taking the necessary steps to return to normal business operations. It is adopted by information security professionals as a strategic approach and is a critical component in enhancing cyber resilience.
Fundamentals of Emergency Management
Incident Response forms the foundation of an organization’s ability to respond quickly to cyber threats. This process aims to reduce risks and ensure operational continuity. It includes the infrastructure and protocols necessary to protect critical information and systems.
Strategic planning plays a major role in this management process; being prepared for both predictable and unpredictable events is fundamental. Developing customized response plans for different scenarios and conducting regular drills are key elements of effective intervention.
Cyber security incidents are increasing by 27% every year.
An effective Incident Response process includes identifying, analyzing, responding to, and subsequently improving the incident. In this complex process, continuously updated threat intelligence and adequate technological tools should be used, and coordination and communication between all team members should be excellent.
Importance of Incident Response Processes
Incident Response (IR) processes represent strategic response mechanisms established to address incidents in the field of cybersecurity. Its importance lies in increasing the resilience and flexibility of organizations in the face of cyberattacks.
- Effective IR Planning: Ensures that security breaches are detected in a timely manner and thoroughly investigated.
- Immediate Response Capacity: Ensures rapid action to limit the impact of an incident and prevent further damage.
- Maintaining Operational Continuity: Supports the rapid return of business processes to normal after an incident and minimizes financial losses.
- Compliance and Regulatory Compliance: Ensures compliance with regulations and reputation management.
- Comprehensive Improvement Strategies: Includes detailed post-incident investigation and measures to prevent recurrence, with a view to improving security posture.
The implementation of these processes plays a critical role in ensuring resilience and compliance against cybersecurity threats.
IR processes enable organizations to take a proactive stance against cyber threats and continuously improve their response capabilities.
Incident Response Phases
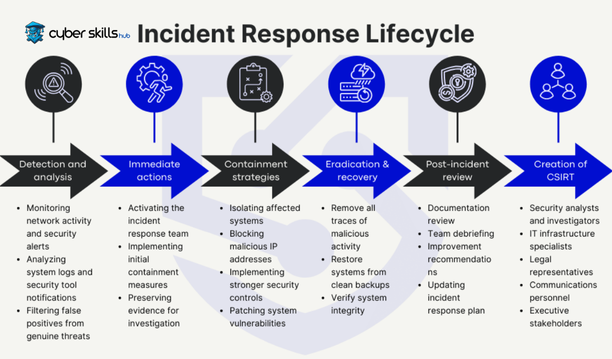
Incident Response is a process that outlines the steps to be taken in a methodological approach from the moment a cybersecurity incident is detected. At its core, there are six main phases: preparation, detection, response, containment, recovery, and post-incident investigation. These phases progress in a coordinated manner to minimize the impact of the cybersecurity incident and build organizational resilience.
Preparation phase includes a comprehensive set of policies and procedures that enhance the company’s ability to respond to incidents. During the detection phase, data and alerts from security systems are analyzed to identify anomalies. This is followed by the response phase, where necessary actions are taken to limit damage and prevent the incident from spreading. During the elimination phase, threat actors are removed from the system. The recovery phase involves restoring systems and affected assets to their previous state and closing any vulnerabilities that have been exposed. Finally, in the post-incident review phase, the incident is analyzed in detail and the necessary information is gathered to develop future security strategies. These phases are critical for effectively managing the incident response process and continuously improving an organization’s security posture.
A solid foundation is essential to respond effectively to cybersecurity incidents. To learn these fundamentals, check out our course titled “Cybersecurity Fundamentals Training.” This course will help you build a solid foundation in cybersecurity and prepare you for the challenges you may encounter in the incident response process.

Role of the Preparation Stage
Preparation phase forms the basis of the incident response process and is the critical first step in an organization’s defense against cyber security breaches. This phase involves designing the plans, policies, and procedures necessary to respond to a potential cyber security incident.
Through a detailed analysis of the corporate structure and assets, the roles and responsibilities of critical personnel are defined. Continuous training of the cybersecurity team, updated emergency communication plans, the creation of an incident response plan, and regular simulated drills are important components of this phase. In this way, the team becomes proficient in response processes and can act quickly at the first signs of an incident.
At the same time, the preparation phase contributes greatly to improving the functional capabilities of the incident response team. This phase includes regularly reviewing cybersecurity devices, software, and other supporting tools; integrating proactive detection mechanisms such as threat hunting and behavior analysis; and strengthening the defense structure, such as firewalls and IDS/IPS systems.
Finally, the preparation phase reflects the order and discipline within an organization and serves as the foundation for establishing a cybersecurity posture, governance, and culture. This phase ensures that employees’ security awareness is increased through awareness programs and user training; compliance with legal, regulatory, and business continuity requirements is ensured; and scenario-based strategic planning is carried out to identify potential weaknesses that may arise during a crisis. This plays a critical role in demonstrating an organization’s cybersecurity capabilities and preventing potential breaches.
Detection and Analysis Processes
During the detection and analysis phase, early identification of suspicious activities and security breaches in the cybersecurity ecosystem is essential. This process involves continuous monitoring and assessment to detect anomalies and potential threats.
In-depth analysis of the threats encountered is of paramount importance in determining the source, impact, and scope of the incident. At this stage, the strategies to be used in responding to the incident are determined, making a detailed analysis process indispensable. The accuracy of the data analyzed directly affects the accuracy of the decisions to be made, requiring a meticulous and methodical approach. Collecting information about attack vectors and threat actors based on identified clues is one of the fundamental components of the analysis process.
Effective analysis requires careful attention to misleading data and false positives. Properly evaluating each alert ensures that false alarms are reduced and that focus remains on real threats. The tools and techniques used at this stage can directly impact the level of detail and speed of the analysis.
As a result, a detailed and accurate analysis process reduces the workload of incident response teams and optimizes response processes. When situations requiring immediate intervention arise, decision-making mechanisms based on analysis results are activated, thereby minimizing potential damage and preventing the spread of threats. Professional analysis tools and accumulated experience play a crucial role in ensuring that detection and analysis processes are carried out thoroughly.
Destruction and Recovery Strategies
The elimination process involves removing malicious software and attack effects from systems. This stage aims to completely eliminate the threat and prevent it from recurring. Recovery strategies involve restoring systems, data, and functions that have been damaged by the attack to their normal state. It is important to regularly create and update backups of critical data and systems.
The removal of malicious software and components from the system is essential for elimination. The complete removal of the threat vector is the primary goal of this process. The recovery process consists of steps necessary to restore normal operations and ensure that systems are once again operating securely. Careful planning and implementation of these steps will increase resilience against similar threats in the future.
Elimination and recovery strategies are shaped based on findings that emerge from a detailed analysis of the incident. These strategies focus on the tactics and techniques used by threat actors and are effective in preventing similar incidents. At the same time, they also entail updating cybersecurity policies and reviewing firewalls and other preventive control mechanisms.
Taking security measures to prevent an asset from being damaged again is one of the cornerstones of successfully completing destruction and recovery processes. These processes are critical to ensuring operational continuity and protecting the principles of confidentiality and integrity. Additionally, they ensure compliance with regulatory and legal requirements, enabling the incident to be closed without leaving a trace and ensuring the system is better prepared to handle similar threats in the future. In other words, destruction and recovery go beyond mere immediate intervention and encompass the continuous improvement of processes.
Role and Training of Experts
Incident Response is a complex process in which cybersecurity experts play a sensitive and dynamic role. This process requires critical decision-making that demands deep technical knowledge. Cybersecurity experts must undergo specialized training in incident identification, analysis, and response. Additionally, they must possess the skills and experience to minimize the impact of these incidents on the organization, as well as strong communication skills.
The training of an effective expert in incident response requires continuous renewal to keep them up to date with the ever-changing threat landscape. The necessary certifications and ongoing training ensure that experts remain competitive and knowledgeable in this rapidly evolving field. Additionally, scenario-based training that focuses on making sound decisions under high pressure, resolving complex issues, and establishing effective communication is critical in this process. All these skills required for cybersecurity experts to develop a robust incident response strategy must be grounded in both theoretical and practical foundations.
Qualifications of Incident Response Specialists
Incident Response experts must have deep technical knowledge and analytical thinking skills. These experts must be able to make quick and effective decisions in the face of complex cybersecurity threats.
In addition, leadership and management skills are critical in incident response processes. The ability to properly direct and motivate teams is essential.
Mastering a wide range of cybersecurity tools and being able to use them effectively in appropriate scenarios is essential for experts to succeed. A good incident response expert should also be able to keep up with the latest threat intelligence and integrate it into strategies.
In addition to having a deep understanding of information technology, an incident response specialist who is well versed in legal requirements and compliance standards can effectively manage risk and crisis communication. These specialists should also play an active role in tracking incidents, reporting, and learning lessons, with the ability to accurately identify threats, respond to them, and plan post-incident recovery steps.
Importance of Continuing Education
Continuous education is essential for cybersecurity professionals to adapt to rapid changes in the industry. As new threats and technologies constantly evolve, professionals in this field must be committed to lifelong learning.
The learning process continues with the updating of cybersecurity standards and protocols. This dynamic structure is an integral part of professional development.
Experts must keep abreast of industry innovations in order to identify new attack vectors, develop strategies to neutralize them, and incorporate innovations into the incident response process. The success of this process requires a continuous and systematic training program, reinforced by simulations and exercises based on real-world incidents.
Continuous training for professionals not only increases knowledge, but also maximizes the effectiveness and speed of response to incidents. Comprehensive training encourages cybersecurity experts to keep their skills up to date in line with evolving threats, thereby playing a vital role in mitigating the severity and impact of an incident. For this reason, ‘best practices’ for incident response must be continuously updated, and experts must be familiar with these changes.
Incident Response Team Structure
Incident Response, or incident response team, is a unit consisting of experts with different skills, established to detect, investigate, and respond appropriately to cybersecurity incidents. The team’s core structure includes roles such as incident manager, security analysts, IT specialists, and legal advisors. This diversity ensures that a comprehensive and effective strategy can be implemented to address any type of security incident.
Each unit within the team has specific responsibilities within its area of activity, and these responsibilities are addressed in an integrated manner at every stage of the incident response process. For example, while the Incident Manager is responsible for coordinating the incident and keeping communication channels open, security analysts conduct detailed analyses to investigate complex security threats and prevent malicious activity. Meanwhile, IT specialists focus on improving the security of existing systems and repairing damaged infrastructure, while legal advisors provide guidance on potential legal obligations and communication strategies. Each element works to maintain the integrity of the team, maximizing the continuity and effectiveness of incident response capabilities.
Cross functional teams
During the incident response process, cross-functional teamwork is of utmost importance. Bringing together individuals from different areas of expertise enables a faster and more comprehensive response to incidents. In fact, this multidisciplinary structure plays a critical role in ensuring a quick and effective response to security breaches.
In addition, these teams are essential in analyzing incidents and in the aftermath. These processes require a high level of coordination and communication, and a comprehensive strategy is developed to serve common goals.
The effectiveness of the incident response team depends on the ability of cross-functional teams to work together seamlessly. Proactive protection and reactive response capabilities contribute to this coordination, ensuring that processes run smoothly.
Each unit undertakes the task of meeting the specific needs of the incident and addressing systemic weaknesses, while also collaborating to achieve common goals. This ensures a rapid and high-quality response.
A cross-functional approach increases flexibility and resilience in the face of security incidents. By creating a dynamic defense mechanism against existing and potential threats, it continuously strengthens the organization’s security infrastructure.
In conclusion, cross-functional teams are essential in the incident response process. These teams play an integral role in managing a security incident and the subsequent recovery process by implementing multi-layered defense strategies.
Communication and Collaboration Strategies
Communication is the backbone of the incident response process.
Effective communication during incident response ensures coordination between various departments. Communication protocols and tools established to enable healthy communication between teams are fundamental to the timely and accurate flow of information. These protocols directly influence the decision-making process in the event of a cybersecurity incident and ensure that the incident is managed effectively.
High-risk events require quick decisions.
Time is critical, and lines of communication must remain open. Incident response teams must have clear communication plans and backup channels in place to ensure effective communication with internal and external stakeholders while preventing information leaks.
The incident response plan should include detailed communication strategies. Adaptable communication hierarchies, information sharing protocols, and crisis communication methods, tailored to the scale of the incident, ensure that all stakeholders have access to the right information at the right time, enabling a rapid and effective response.
Frequently Asked Questions About Incident Response
What is Incident Response?
Incident Response is a strategic management process developed to prepare for cyber security breaches and other security incidents and respond to them quickly and effectively.
What is the importance of the Incident Response process?
The incident response process increases organizations’ resilience against cyber attacks, minimizes damage, and ensures rapid resolution of incidents, thereby maintaining business continuity.
What phases are involved in the incident response process?
The incident response process consists of six main phases: preparation, detection, response, containment, recovery, and post-incident investigation. Each phase contributes to managing the incident and preventing future incidents.
What are the qualifications of an Incident Response specialist?
An Incident Response Specialist must have in-depth technical knowledge and analytical thinking skills, be able to use cybersecurity tools effectively, and make the right decisions under high pressure. Leadership and management skills are also important for this role.
Why is continuous training important in the incident response process?
Due to the constant evolution of cyber threats, Incident Response experts must be equipped with up-to-date information. Continuous training is critical for experts to identify new threats and develop effective response strategies.
What is the role of cross-functional teams in the Incident Response process?
Cross-functional teams bring together individuals from different areas of expertise to enable a faster and more comprehensive response to security incidents. These teams provide the coordination and diversity necessary for effective management of cybersecurity incidents.







