Currently Empty: $0.00

How do you feel when cyber attackers sneak a virus into your network?
Honeypots can be thought of as a cunning cybersecurity scam. They are artificial target systems that lure attackers into their domain, like a jar filled with sweets that you place in front of your house. However, the goal here is not to sweeten them, but to gather information by observing their strategies and behaviors, and to strengthen your defenses against future attacks.
Honeypot Term and Main Functions
Honeypot is a security tool built on information gathering and decoying among cyber defense mechanisms. These systems are deliberately left vulnerable and monitored to lure potential attackers and reveal their attack methodologies.
The main function of these spoofing systems is to detect attacks at an early stage, allowing cybersecurity teams to analyze real threats. In this way, honeypots can become a rich source of data to understand hackers’ attack vectors, the tools they use and system vulnerabilities.
In short, honeypots present deliberately crafted, controlled vulnerabilities that attract attackers’ attention and lure them into their traps. This plays a critical role in updating cyber defense strategies and developing effective security measures.
Definition and History of Honeypot
Honeypot is a type of trap system in cybersecurity that lures potential attackers onto itself to observe their behavior. These artificial targets are designed to contain security vulnerabilities. In this way, in-depth information about enemy tactics and attack methods can be obtained.
Honeypots, which have been in use since the mid-1980s, are a pioneering concept in the field of information security. One of the main strategies is to create “target” systems to protect real resources. Environments with potential risk were deliberately created to obtain useful statistics and attack analysis.
Honeypots are indispensable tools in cyber security as early warning systems.
These systems are essentially divided into low-interaction and high-interaction systems. Low-interaction honeypots set simple traps, while high-interaction ones have a realistic and detailed configuration. This distinction allows security researchers to choose the appropriate type of honeypot based on the level of risk involved.
To better understand the basics of honeypot systems and their role in security, you can check our Cyber Security Basics Tutorial.
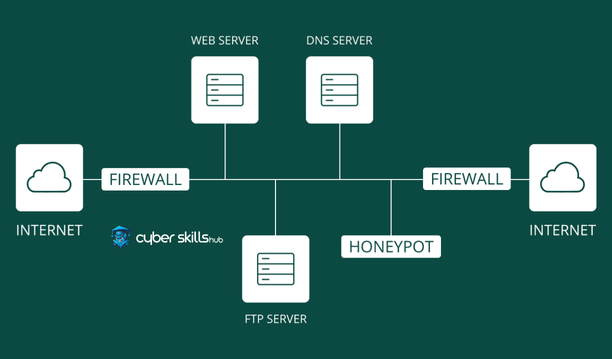
Various Honeypot Types
The diversity of dynamic artificial trapping systems is vital.
There are honeypots that are shaped according to the intended use. Low-interaction honeypots are typically used for standard threats and automated attacks, require few resources and are easily managed. High-interaction honeypots are suitable for more complex and in-depth investigations, mimic replicas of real systems and allow attackers to interact in a more believable environment.
Divided by manufacturer; commercial and open source.
Commercial honeypots are usually easier to manage and provide support services. Open source honeypots, on the other hand, are cost-effective and are continuously improved with contributions from the community. They are also customizable, providing researchers with flexible solutions.
Finally, it can be divided into research honeypots and production honeypots. Research honeypots are used to understand new threat types, attack behaviors and techniques. This type is especially preferred in academic and research-oriented studies. Production honeypots, on the other hand, offer a more practical configuration that is preferred to increase the security level of corporate networks and to react quickly to attacks.
If you want to learn how the threat intelligence collected by honeypots is used, you can take a look at our article on Cyber Threat Intelligence Training.
Basic Functions and Uses
Honeypots are systems designed to deliberately fool cyber attackers. These systems attract attackers by pretending to be real targets.
In terms of network security, honeypots monitor suspicious traffic flow and act as an early warning mechanism. They provide valuable information to cyber security teams by detecting potential threats.
In addition, honeypots are also used to gather information about attack methods. By analyzing the pace of the attacker, the tools they use and the paths they follow during the attack, it makes it possible to strengthen security measures.
In some cases, defense systems use honeypots for counterintelligence purposes. By carefully monitoring the movements of attackers once an attack has begun, important intelligence can be gathered that will contribute to the broader cybersecurity strategy.
In a nutshell, the most important function of honeypots is that they serve as a kind of cyber trickster. They help gather valuable security information and increase the defensive capabilities of organizations.
To see the various types of cyberattacks and examples that can be detected with honeypots, see Cyber Attack Examples: Which Types are Dangerous?
Honeypot Installation Process and Configuration
The honeypot installation process is a critical stage in the implementation of an effective cyber deception strategy. First, a suitable honeypot type is selected for the system to be analyzed. Low-interaction honeypots provide simple emulations, while high-interaction honeypots offer much more detailed simulations of real systems. The selected honeypot software is then installed and configured on dedicated servers or virtual machines. It is crucial that the installation is done within a security network and isolated from real systems to minimize potential risks.
In the configuration phase, the honeypot system needs to be configured in such a way that it attracts attackers but does not damage the real network infrastructure of the organization. In this context, the operating system, network settings and the level of services are important; it is recommended to use reverse-peleology methods, adding decoy files, services or points that appear to be open to attract attackers. It is also essential to enable the necessary logging and monitoring tools to record and analyze the interactions that take place on the honeypot system.
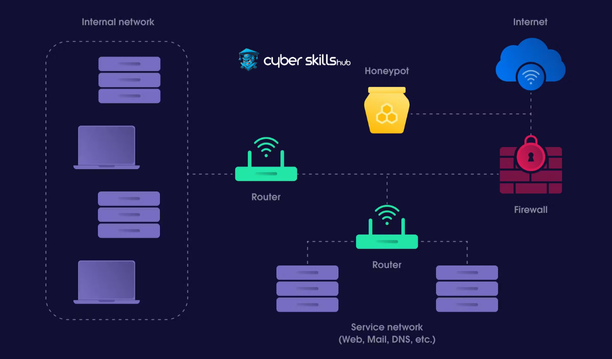
Requirements Analysis and Planning
Requirements analysis prior to honeypot installation is a factor that directly affects the success of the project. The analysis process determines the objectives and scope of the system.
In this analysis, the current state of the organization’s cyber defense infrastructure and the level of integration of the honeypot solution with the existing system should be considered. Customized threat scenarios and targeted attack types are defined at this stage.
Another important step is to plan the resources that will be used to maximize the honeypot’s deception and entrapment capabilities. Server specifications, network topology and other technical details should be analyzed in detail here.
During the planning phase, the roles and responsibilities of the teams that will manage the honeypots should also be clarified. The presence of trained personnel and the distribution of roles is critical for the effective functioning of the system.
Finally, determining the budget for the project and allocating resources is the final step in the requirements analysis and planning process. This ensures the financial sustainability of project success.
To learn about the relationship between honeypots and penetration tests and their place in security strategies, read our article, Penetration Tests: How They Secure Your Internet?
Hardware and Software Justifications
Hardware and software choices in the design of honeypot systems directly affect system performance and reliability. A flexible and updatable infrastructure enables adaptation to unpredictable attack scenarios.
- Processor and Memory: High processing power and sufficient memory capacity allow honeypot systems to respond quickly to complex attacks.
- Storage Space: Large and reliable storage is required for ingested data and logs.
- Network Cards: Multiple network interfaces increase network eavesdropping and intrusion detection capabilities.
- Isolation Mechanisms: Virtualization and container technologies isolate honeypot systems and facilitate control.
- Automatic Updating: Automating security patches and software updates increases the resilience of systems to current threats.
In particular, key locations in networks should be hardware and software optimized to strengthen data collection and analysis capabilities.
As software, the honeypot system directly contributes to cyber threat intelligence through its ability to understand and respond to events. Therefore, software platforms that support advanced cyber threat detection algorithms are needed.
Honeypot Management and Maintenance
Effective management of honeypot systems is critical to the successful implementation of security policies. These systems require regular updates and maintenance, otherwise they can lose their reliability. Continuous updating and monitoring of these systems is essential to maintain the security and long-term effectiveness of Honeypot.
Configuration changes, system patches and security updates help honeypot systems to continuously provide the necessary defense against the latest threats. For effective management, it is important to establish manual auditing processes as well as automatic update mechanisms. In addition, regular evaluation of the data obtained during intrusion detection and analysis processes provides information that can be used to further improve honeypot systems.
Analyzing the data collected by honeypots provides cyber security experts with valuable information about attack patterns and vulnerabilities. An integrated analysis of data collected from inside and outside the system makes detection and response processes more effective. Thanks to these analyzes, honeypot systems play a critical role in taking preventive measures not only against current threats, but also against possible future attacks. Detailed analysis of the data enables a better understanding of attack methods and enables defense strategies to be shaped accordingly.
In summary, the effectiveness of honeypot systems depends on keeping them constantly updated, monitoring them and carefully analyzing the data obtained. These processes provide cybersecurity experts with in-depth knowledge and help organizations to be better prepared against cyber threats. Therefore, the management and maintenance of honeypots should be considered an essential part of a cybersecurity strategy.
To understand how honeypots can play a role in enterprise networks and operational technologies, What is Operational Technology? What are Safety Precautions? check our article.
Frequently Asked Questions about Honeypot
What is Honeypot?
A honeypot is a trap system that is deliberately created to catch cyber attackers and make them appear vulnerable. These systems are used to observe the behavior of attackers and improve security measures.
What are the main functions of honeypots?
Honeypots are used to detect attacks at an early stage, analyze the methodologies used by attackers and monitor potential threats. In this way, they provide valuable information to cyber security teams.
What are the types of honeypot?
There are two main types of honeypots: low-interaction and high-interaction. Low-interaction honeypots are used to detect simple attacks, while high-interaction honeypots provide more complex and detailed analysis.
How does the honeypot installation process work?
The honeypot installation process starts with the selection of a suitable honeypot type and continues with the installation of honeypot software on dedicated servers or virtual machines. The system is configured to contain deliberate vulnerabilities to attract attackers.
How to manage and maintain the honeypot system?
Honeypot systems require regular updates and maintenance. In order to maintain the security of the system and maintain its effectiveness, it must be continuously monitored and necessary security updates must be made. The data obtained is regularly analyzed and this analysis helps to develop security strategies.
What information do honeypots collect?
Honeypots collect a variety of information about attackers, such as their frequency of use, preferred tools, targeted vulnerabilities and attack methods. This information is critical in developing cyber security strategies.
Can honeypots detect all types of attacks?
Honeypots are very effective at detecting the type of attacks for which they were specifically designed, but they may not be sufficient on their own to detect every type of attack. This is why they are often used in combination with other security systems.
Are there risks of using honeypots?
The main risks of using honeypots are that, if misconfigured, attackers can recognize these systems and direct attacks against real systems. Therefore, honeypots need to be carefully managed and monitored.







